So when was the last time you stepped out to buy something from an offline store? It has probably been a while, right? With the advent of e-commerce it has become inevitable that you expect everything to be available online, ordered and delivered to you.
Let’s first define E-commerce
- The conduct of selling, buying, logistics, or other organization-management issues on the WEB.
OR
- Technology mediated exchanges between parties (individuals and/or organizations) as well as the electronically based intra- or inter-organizational activities that facilitate such exchanges
Types of E-Commerce:
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce: customers deal directly with the organization, avoiding any intermediaries. Example: Amazon, Blibli
- Business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce: participants are organizations. Example: Grainger, Alibaba
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce: participants are individuals, with one serving as the buyer and the other as the seller. Example: Olx
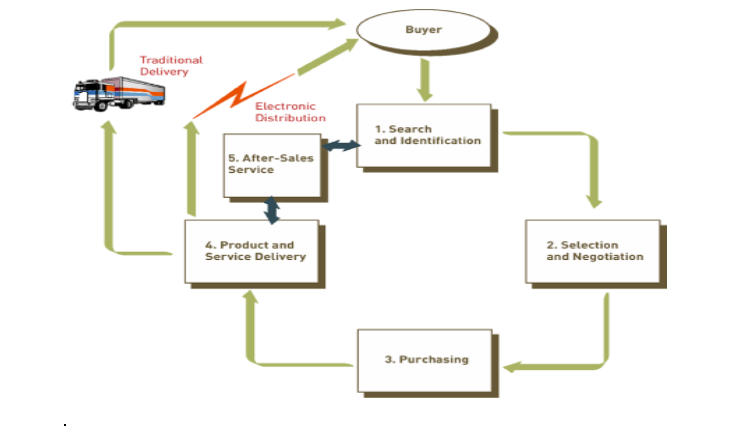
Multistage Model for E-commerce:
A multistage model for e-commerce includes
- Search and identification
- Selection and negotiation
- Purchasing
- Product or service delivery and
- After-sales service
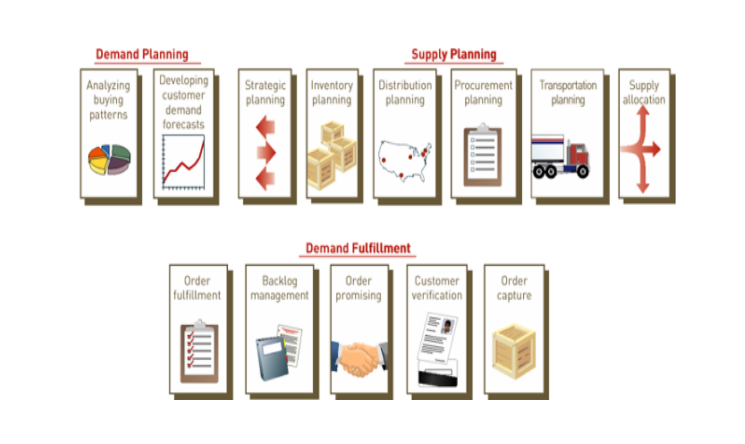
The E-Commerce Supply Chain:
Supply chain management is a key value chain composed of:
- Demand planning
- Supply planning
- Demand fulfillment
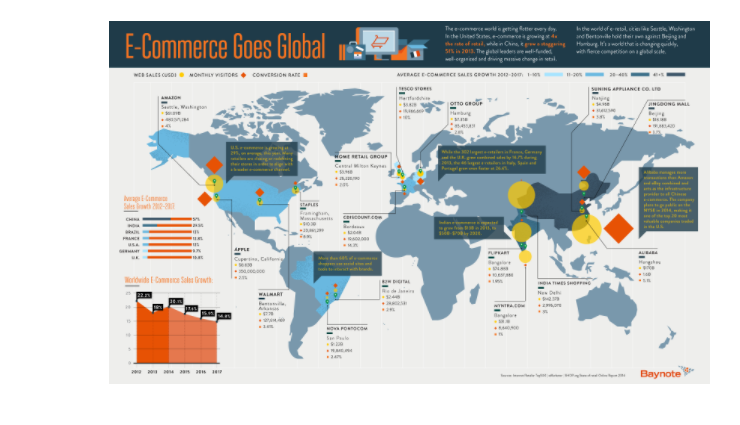
Global E-Commerce
Localization: Adapting an existing country centric web site to another language and culture
Steps involved in localization
- Recognizing and conforming to the nuances, subtleties, and tastes of local cultures
- Supporting basic trade laws such as those covering each country’s currency, payment preferences, taxes, and tariffs
- Ensuring that technological capabilities match local connection speeds
- Determine which global markets make the most sense for selling products or services online
- Decide whether Web content should be generated or updated centrally or locally
Marketing
- Market segmentation: the identification of specific markets to target them with advertising messages
- Technology-enabled relationship management: use of detailed information about a customer’s behavior, preferences, needs, and buying patterns to set prices, negotiate terms, promotions, add product features, and otherwise customize the entire relationship with that customer
E-commerce Advantages
- Ability to reach new markets
- Reduces costs (for some businesses)
- Increased purchasing opportunities
- More efficient (electronic payments, telecommuting, etc.)
E-commerce Disadvantages
- Incompatibility for certain industries, e.g. heavy machinery
- Limitations of the medium
- Operational costs
- Skills required
- Cultural and legal issues
Reference:
Online Book : Principles of Information System A managerial Approach Seventh Edition And Google Images on “E-commerce growth in world”
By Avni Sharma
Engati – www.engati.com – A Coviam technologies platform
Coviam Technologies
www.coviam.com